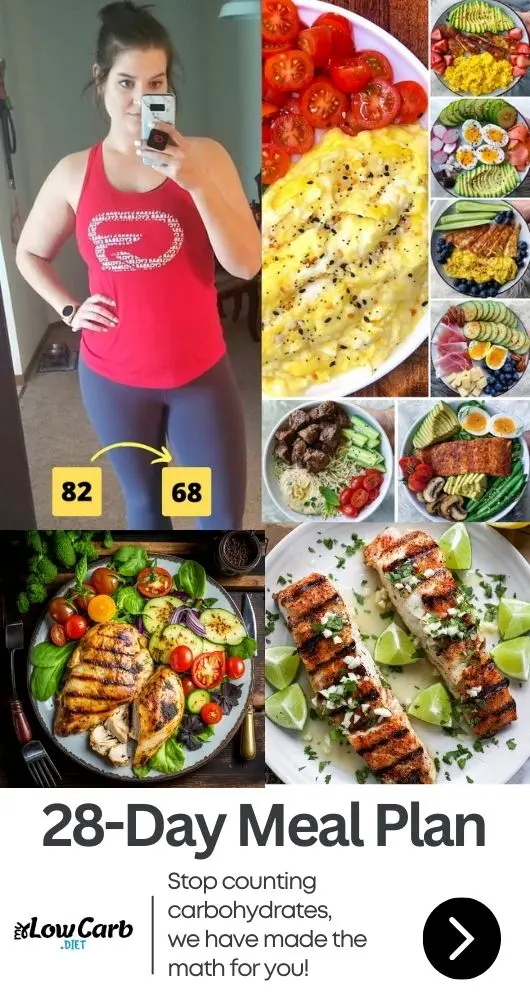
In the world of sports and athleticism, diet plays a pivotal role in an athlete’s performance and recovery. “The Athlete’s Guide to Low-Carb Eating: Boosting Performance and Accelerating Recovery” dives into the often-misunderstood realm of low-carbohydrate diets for athletes. This guide aims to shed light on how a low-carb diet can not only fuel an athlete’s performance effectively but also enhance their recovery process.
Traditionally, athletes have leaned heavily towards high-carbohydrate diets, with the belief that carbs are the primary source of energy. However, recent research and emerging trends in sports nutrition have started to challenge this notion. Low-carb diets, contrary to popular belief, can be incredibly effective in optimizing an athlete’s energy levels, endurance, and muscle recovery.
This introduction sets the stage for a deeper exploration into the mechanics of a low-carb diet, its impact on athletic performance, and the potential benefits it holds for athletes across various disciplines. From debunking common myths to understanding the science behind low-carb eating, this guide provides comprehensive insights into how athletes can harness the power of a low-carb diet to reach their peak performance and accelerate recovery times.
Introduction to Low-Carb Eating for Athletes
In the competitive world of sports, athletes continually seek nutritional strategies that can enhance their performance and recovery. The concept of low-carb eating, often overlooked in athletic circles traditionally dominated by high-carb diets, is gaining traction for its potential benefits in this area.
The Misunderstood Role of Carbohydrates: Traditionally, carbohydrates have been viewed as the primary fuel source for athletes, especially for endurance sports. However, this perspective is evolving. While carbs play a critical role in energy production, their overconsumption, especially of refined carbs, can lead to various issues like energy spikes and crashes.
Adapting to a Low-Carb Diet: Transitioning to a low-carb diet doesn’t mean eliminating carbs entirely. It involves reducing the intake of high-carb foods like bread, pasta, and sugary snacks, and replacing them with healthier options. This shift encourages the body to use fat as a primary energy source, leading to more sustained energy levels and potentially better fat burning during exercise.
Benefits for Athletes: For athletes, a well-planned low-carb diet can offer several advantages. These include improved energy management, enhanced fat burning, reduced body fat levels, and potentially lower inflammation. Moreover, for endurance athletes, adapting to a low-carb diet can lead to improved efficiency in using fat as fuel, which is a more abundant energy source compared to carbohydrates.
Debunking Myths: One common myth is that athletes need a high-carb diet for high-intensity training. While carbs can benefit high-intensity performance, this doesn’t preclude the effectiveness of a low-carb diet. Strategic intake of carbs, particularly around training sessions, can complement a low-carb approach, offering the best of both worlds.
Individualized Approach: It’s crucial to remember that there’s no one-size-fits-all solution in nutrition. What works for one athlete may not work for another. Factors like the type of sport, training intensity, and individual metabolic responses play a significant role in determining the ideal dietary approach.

The Science Behind Low-Carb Diets and Athletic Performance
The relationship between low-carb diets and athletic performance is a subject of growing interest and research in the sports nutrition world. This section explores the scientific principles underpinning low-carb diets and how they can potentially impact an athlete’s performance.
Understanding Energy Systems: The human body uses different energy systems during exercise, primarily carbohydrates (glycogen) and fats. Traditional high-carb diets emphasize glycogen as the main energy source. However, low-carb diets shift the focus to fats, utilizing the body’s abundant fat stores for energy, which can be especially beneficial in endurance sports.
Ketosis and Athletic Performance: A key aspect of low-carb diets is the state of ketosis, where the body, in the absence of sufficient carbohydrates, starts to burn fat for fuel, producing ketones. Research suggests that ketosis can provide a more constant energy supply, reducing the risks of energy fluctuations common with high-carb diets.
Muscle Preservation and Endurance: Low-carb diets can aid in muscle preservation due to the body’s reliance on fat for energy, reducing the need to break down muscle for glucose. This is particularly advantageous for endurance athletes, who often engage in prolonged physical activity.
Adaptation Period and Performance: Athletes transitioning to a low-carb diet often experience an adaptation period, where performance might temporarily decline as the body adjusts to using fat as the primary energy source. However, studies indicate that once adapted, athletes may experience enhanced endurance and steadier energy levels.
Balancing Macronutrients for Optimal Performance: While a low-carb approach can benefit athletic performance, it’s essential to balance it with adequate protein and healthy fats to ensure overall nutritional needs are met. This balance supports muscle repair, energy production, and overall health, crucial for any athlete’s performance.
Low-Carb Eating for Enhanced Recovery
Recovery is a crucial component of an athlete’s training regime, and nutrition plays a significant role in this process. This section discusses how a low-carb diet can be beneficial for an athlete’s recovery.
Reducing Inflammation: One of the key benefits of a low-carb diet is its potential to reduce inflammation. Chronic inflammation can slow down recovery and increase the risk of injuries. Diets low in processed carbohydrates and sugars have been shown to lower inflammation markers, aiding in quicker recovery.
Improved Quality of Sleep: Carbohydrate intake, especially in the form of sugars and refined carbs, can impact sleep quality. A low-carb diet, particularly when coupled with an adequate intake of healthy fats and proteins, can lead to more restful and restorative sleep, which is essential for recovery.
Enhanced Muscle Repair: Protein is a critical nutrient for muscle repair, and low-carb diets often emphasize high-quality protein sources. This focus helps in the efficient rebuilding and repairing of muscle tissues damaged during intense workouts.
Stabilizing Energy Levels: Fluctuating energy levels can impede recovery. A low-carb diet helps stabilize blood sugar levels, which can lead to more consistent energy throughout the day. This stability is crucial for allowing the body to focus on recovery processes.
Optimizing Hormonal Balance: Nutrition plays a vital role in hormonal balance, which is essential for recovery. Low-carb diets can help regulate hormones like insulin and cortisol, which in turn can positively impact recovery and overall athletic performance.
Balancing a Low-Carb Diet with Training Needs
For athletes, striking the right balance between their diet and training requirements is key to achieving optimal performance. This section addresses how athletes can effectively integrate a low-carb diet into their training regimen.
Understanding Individual Energy Needs: Every athlete has unique energy needs based on their sport, training intensity, and personal metabolism. It’s important for athletes to assess their own energy requirements and adjust their carb intake accordingly. This might mean higher carb intake on intense training days and lower on rest or light training days.
Timing of Carb Intake: While maintaining a low-carb diet, the timing of carbohydrate intake can significantly impact performance. Consuming carbs strategically before, during, or after high-intensity training sessions can provide the necessary energy boost without deviating from the overall low-carb approach.
Incorporating Nutrient-Dense, Low-Carb Foods: Focusing on nutrient-dense, low-carb foods ensures that athletes get essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Foods like leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and lean proteins should be staples in an athlete’s diet.
Hydration and Electrolyte Balance: A low-carb diet can sometimes lead to changes in fluid and electrolyte balance. Athletes should pay extra attention to hydration and possibly supplement with electrolytes to maintain optimal performance and recovery.
Listening to the Body: Finally, the most crucial aspect of balancing a low-carb diet with training is listening to one’s body. Athletes should monitor their energy levels, performance metrics, and overall wellbeing, and be willing to adjust their diet as needed.

Success Stories and Case Studies
The proof of any dietary approach lies in its real-world application and outcomes. In this section, we explore case studies and success stories of athletes who have adopted a low-carb diet and witnessed significant improvements in their performance and recovery.
Endurance Athletes and Low-Carb Success: Numerous endurance athletes have reported improved performance and faster recovery times after switching to a low-carb diet. These athletes often note greater energy stability during long events, less reliance on frequent carbohydrate refueling, and quicker recovery post-competition.
Strength and Power Athletes: While endurance athletes have been the primary focus in low-carb diet studies, strength and power athletes also report benefits. These include better body composition, leaner muscle mass, and reduced inflammation, leading to better overall performance.
Adaptation Stories: The transition to a low-carb diet can be challenging. Case studies often highlight the adaptation phase, where athletes might experience temporary dips in performance. However, with persistence, many athletes report a remarkable improvement in energy levels and endurance.
Personalized Nutrition Plans: These success stories also underscore the importance of personalizing the diet to fit the athlete’s specific needs. What works for one athlete might not work for another, emphasizing the need for individual assessment and adjustment.
Medical Supervision and Professional Guidance: Finally, these case studies highlight the importance of undertaking dietary changes under medical supervision and with professional guidance, especially for athletes with specific health conditions or nutritional requirements.
The Low Carb Diet is a nutritional strategy that emphasizes reducing the intake of carbohydrates. This dietary approach is known for its potential to help control blood sugar levels, support weight loss, and improve overall metabolic health. By limiting carbs and focusing on foods like lean proteins, vegetables, and healthy fats, individuals may experience better appetite control and more stable energy levels.
Conclusion
“The Athlete’s Guide to Low-Carb Eating: Boosting Performance and Accelerating Recovery” has journeyed through the multifaceted aspects of low-carb diets in the context of athletic performance and recovery. We’ve explored the scientific rationale, the benefits for recovery and performance, practical tips for integrating this diet into training regimens, and inspiring success stories from the athletic world.
As we conclude, it’s important to reiterate that while a low-carb diet can offer numerous benefits for athletes, it is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The key is personalization, understanding individual energy needs, and adjusting the diet to fit those needs in alignment with training and performance goals.
Nutrition is a powerful tool in an athlete’s arsenal. When used wisely and tailored to individual requirements, it can significantly enhance performance and accelerate recovery. Whether you’re an endurance runner, a strength athlete, or somewhere in between, considering a low-carb approach might just be the game-changer you need.